How to Use

What is FSDT?
There are two main categories of spatial data, namely Framework Spatial Data Theme (FSDT) and Common Sharable Spatial Data (CSSD).
- FSDT provides a standard geographic framework for geocoding or referencing other datasets.
- CSSD is demanded by multiple agencies and/ or members of the public for use in their spatial analysis or applications.
FSDTs are now available on the CSDI Portal.
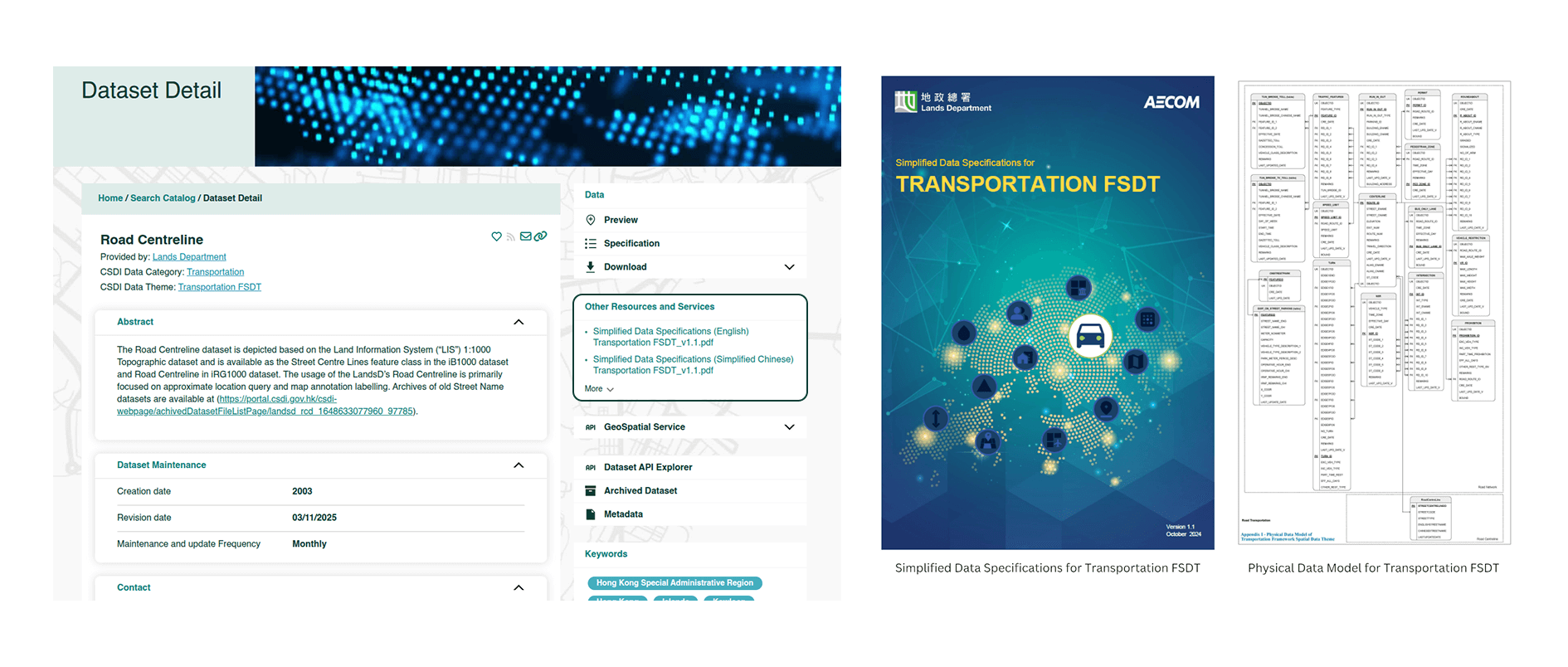
Dataset documentation and specifications
Unlike other datasets, datasets categorised as FSDTs are supplemented with A Simplified Data Specifications (SDS) to provide additional information, such as definition of datasets and entities, as well as B physical data model that outlines the relationships within the FSDT.
Users could download the SDS document from the respective datasets under the column "Other Resources and Services". The SDS is available in English, Traditional Chinese, and Simplified Chinese to facilitate access for data users in different languages.
Additionally, users could preview the spatial dataset and access the dataset using the Geospatial Services for all FSDTs.
How to link up the data?
FSDT establishes linkages between different datasets within the same theme, across different themes, or with CSSDs.
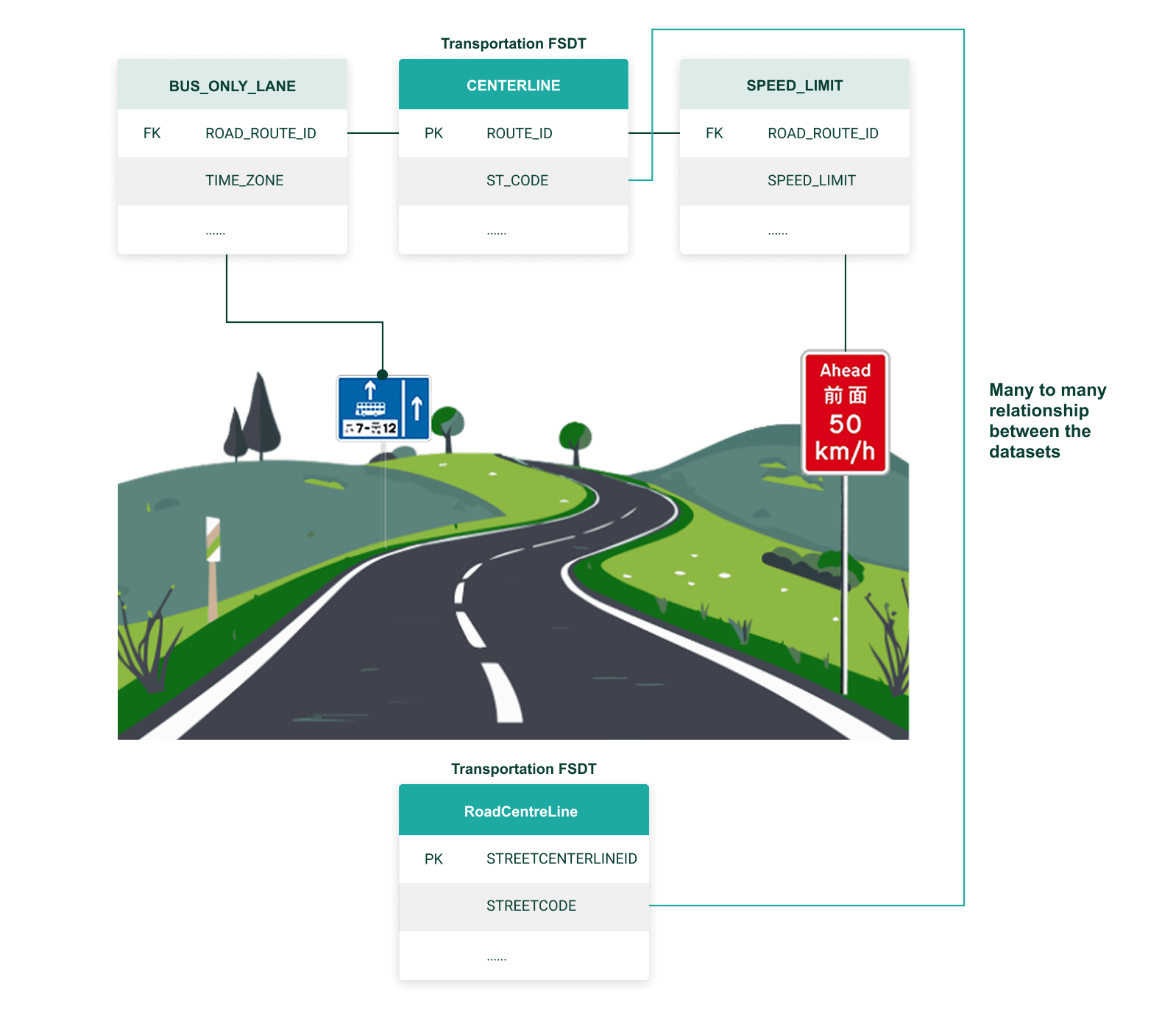
Linkages between entities can be established using Primary Keys (PK) and Foreign Keys (FK). The PK uniquely identifies a record in the entity while the FK, if not null, could match the PK of another entity. The indication of PK and FK in the Entity-Relationship diagrams (ER diagrams) that presented in the physical data model of each FSDT facilitates the determination of spatial relationships and maintains data integrity as the keys remain constant for a specific feature even if other attributes change.
Entities in each dataset may be represented as either feature layers or data tables. To link entities within the ‘Road Network’ dataset, users can refer to the physical data model of Transportation FSDT to identify the respective PK-FK relationships between the entities and join them for specific applications. For example, the 'ROUTE_ID' field of the ‘CENTRELINE’ entity as the PK, can establish multiple relationships with other entities that share the respective 'ROAD_ROUTE_ID' field as the FK. In the Transportation FSDT, there are two datasets, namely 'Road Centreline' and 'Road Network' which are sourced from different data providers. As presented in the physical data model of Transportation FSDT, these datasets can establish a many-to-many relationship through ‘STREETCODE’ (or ‘ST_CODE’).
Use Case 1
Below demonstrates some potential use cases incorporating the new FSDTs with other FSDTs and/ or CSSDs.
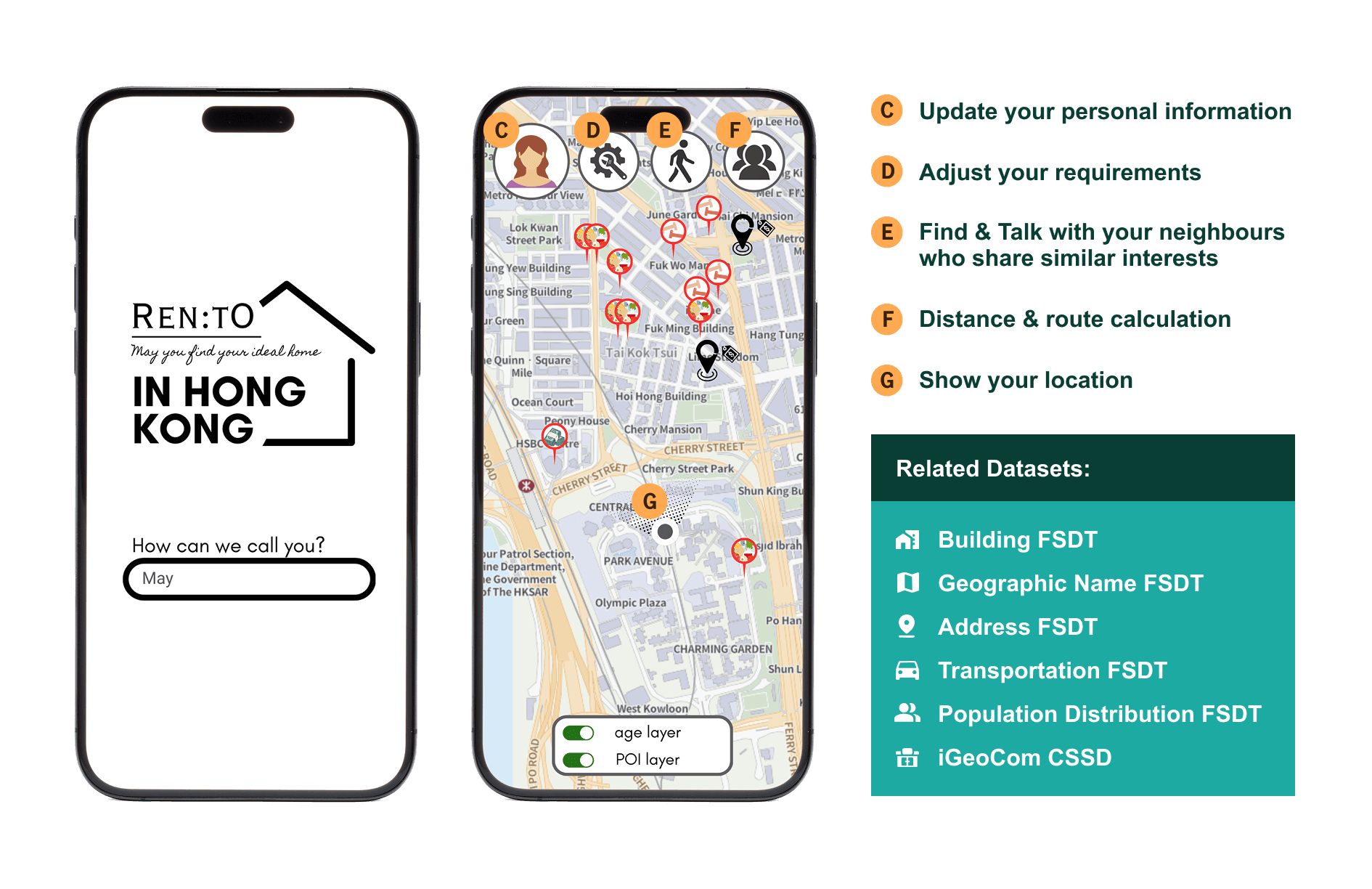
Case 1 - Housing Rental Platform
Related FSDTs: Building, Transportation and Population Distribution
Objective: Develop a housing rental platform featuring a tailored search engine that enables easy and effective property searches, meeting users' expectations.
As an international city, Hong Kong attracts visitors and foreign workers/students to experience its vibrant atmosphere. However, with a wide array of housing options, finding accommodation that perfectly suits their needs can be challenging when moving to an unfamiliar environment.
To address this, a platform could be developed that integrates data from the Population Distribution, Building and Transportation FSDTs, along with community information from the iGeoCom dataset — such as the locations of gym rooms, libraries, parks and museums. This would effectively match the interests, lifestyles, and needs of prospective tenants. With interactive maps and visual data aids in understanding complex information intuitively, it can help users find a community that aligns with their lifestyle, making their transition smoother and more informed.
Reference CSDI Award Case:
https://csdigeolab.gov.hk/images/CSDI_Awards_2024/brief/C4-48.pdf
Use Case 2
Case 2 - Green Recycling
Related FSDT: Population Distribution
Objective: Utilise Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and spatial data for planning and governing effective waste management in Hong Kong
Hong Kong, a city with a high-density population, faces significant challenges in managing its substantial domestic waste. With the aid of GIS and the availability of spatial data, evidence-based governance can be improved. Additionally, providing the public with easy access to recycling stations may encourage greater participation in green initiatives.
Population density datasets, including those grouped by smaller subunit areas, can be analysed alongside recycling-related datasets, such as the Open Space Database of Recycling Stations, to assess the proximity and adequacy of recycling facilities, identifying areas for improvement.
This approach can also foster community involvement and raise awareness about sustainability, helping residents adopt more eco-friendly habits. Ultimately, these improvements support Hong Kong's goal of becoming a greener city for future generations.
Reference CSDI Award Case:
https://csdigeolab.gov.hk/images/CSDI_Awards_2024/brief/C4-72.pdf
Use Case 3
Case 3 - Walk About
Related FSDTs: Address and Building
Objective: Empower spatial data to foster a new, healthy lifestyle through tailored walking experiences and community engagement.
Nowadays, people are increasingly concerned about not only their physical health but also their mental well-being.
The term 'Walk About' has gained popularity as a way to achieve relaxation and maintain mental balance. Walk About is not confined to urban areas; it also encompasses rural locations for deeper exploration of Hong Kong. A platform that aggregates various walking routes by considering spatial data from both 2D and 3D aspects—such as 2D address data and building name data from the Address FSDT and Building FSDT respectively, alongside 3D data from the 3D Pedestrian Network and 3D Visualisation Map for analysing road conditions and accessibility—could be generated to meet users’ expectations. This platform could also incorporate thematic datasets related to heritage, nature, and vibrant city life, including points of interest from the iGeoCom dataset.
The platform can recommend optimal walking routes to enhance the overall user experience. Additionally, it can highlight local businesses situated along these paths, fostering community engagement and encouraging users to support their local shops and services.
Reference CSDI Award Case:
https://csdigeolab.gov.hk/images/CSDI_Awards_2024/brief/C4-43.pdf